Sin X Pi 2 Identity

USEFUL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES USEFUL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES De nitions tanx= sinx cosx secx= 1 cosx cosecx= 1 sinx cotx= 1 tanx Fundamental trig.
An example of a trigonometric identity is. \sin^2 \theta + \cos^2 \theta = 1. sin2 θ+cos2 θ = 1. In order to prove trigonometric identities, we generally use other known identities such.
The sine of ninety degrees minus theta identity is mainly used in two cases in trigonometry. It is used to simplify the sine of ninety degrees minus theta function as the cosine of.
Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a math tutor.
for the "true" proof you need to use matrice, but this is acceptable : sin(a + b) = sin(a)cos(b) +cos(a)sin(b) sin( π 2 + x) = sin( π 2) ⋅ cos(x) + cos( π 2) ⋅ sin(x) sin( π 2).
Purplemath What is an identity? In mathematics, an "identity" is an equation which is always true, regardless of the specific value of a given variable. An identity can be.
sin(2π− x) sin ( 2 π - x) Apply the difference of angles identity. sin(2π)cos(x)−cos(2π)sin(x) sin ( 2 π) cos ( x) - cos ( 2 π) sin ( x) Simplify the expression. Tap for more steps...
An interesting trigonometry problem -- featuring roots of unity. YouTube. More Videos. (sin(x))2 ⋅ ((cot(x))2 + 1) cos(π) tan(x) cos(3x + π) = 0.5. cot(x)sec(x) sin(x) sin( 2π)
Sine, cosine and tangent are the primary trigonometry functions whereas cotangent, secant and cosecant are the other three functions. The trigonometric identities are based on all.
More clearly, we can think of the functions as the values of a unit circle. The above figure shows that the sine and cosine functions repeat every time we go around the unit circle..
How do you use a double-angle identity to find the exact value of sin 120°? How do you use double angle identities to solve equations? How do you find all solutions for sin2x =.
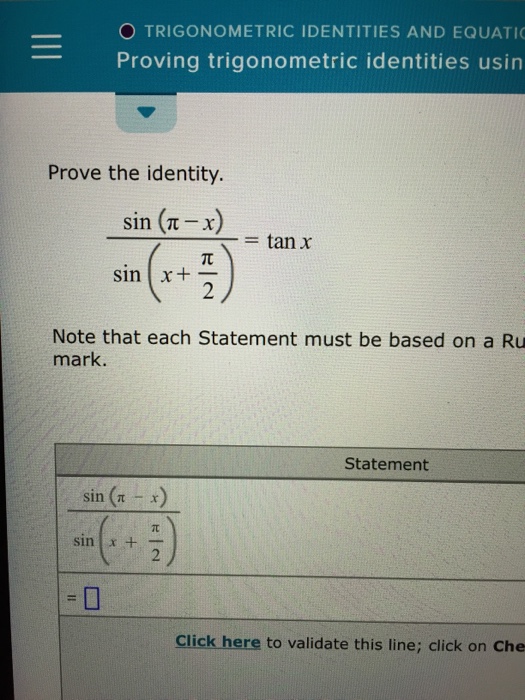
Prove the identity.sin (x+ (pi/2))/sin (pi-x) Note that each Statement must be based on a Rule chosen from the Rule menu. To see a detailed description of a Rule, select the.
Popular Problems Trigonometry Expand the Trigonometric Expression sin (pi/2-x) sin( π 2 − x) sin ( π 2 - x) Apply the difference of angles identity. sin( π 2)cos(x)−cos( π 2)sin(x) sin.
Mar 18, 2016. Apply the sum identities. sin( π 2 − x) = sin( π 2).cosx −cos( π 2).sinx = cosx. because sin( π 2) = 1 and cos( π 2) = 0. sin( π 2 + x) = sin( π 2).cosx.
2: 3-\pi: e: x^{\square} 0. \bold{=} + Go. Steps ... \sin^2(x) Show More; Description. Simplify trigonometric expressions to their simplest form step-by-step. trigonometric-simplification.
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. For math, science, nutrition, history ...
Explanation: cos(( π 2) +x) = cos( π 2)cosx −sin( π 2)sinx. cos( π 2) = 0 sin( π 2) = 1. cos(( π 2) +x) = cos( π 2)cosx0 − sin( π 2)1 sinx. = − sinx. Answer link.
Verify the Identity sin(x+pi/2)=cos(x) Step 1. Start on the left side. Step 2. Apply the sum of angles identity. Step 3. Simplify the expression ... The exact value of is . Step 3.1.2..
We must consider our knowledge of transformations: f (x −α) is a translation of f (x) by (α,0) So hence: sin(x − π 2) is just sinx translated by ( π 2,0) We see that sinx:.
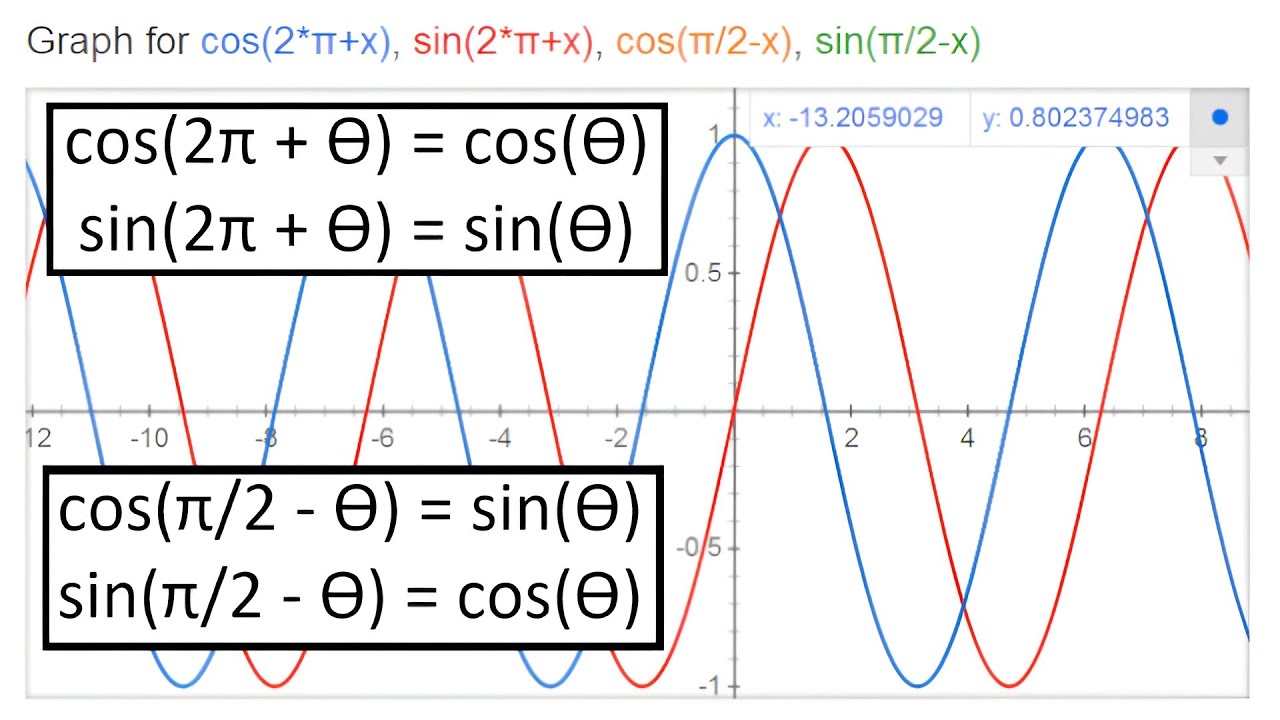
so sin(π 2 − x) = cos(x),. The two identities. cos(π 2 − x) = sin(x) and sin(π 2 − x) = cos(x) are called cofunction identities. These two cofunction identities show that.
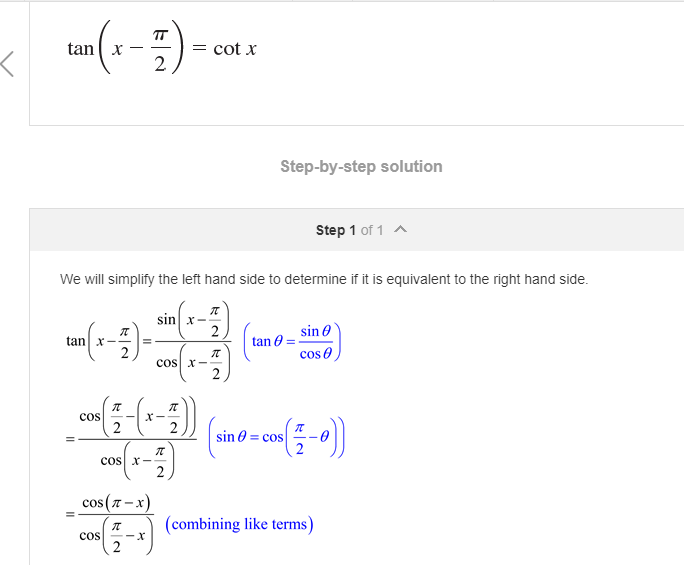
Asked 10 years, 11 months ago. Modified 23 days ago. Viewed 2k times. 5. Show that. cos(x − π 2) = sin x. cos ( x − π 2) = sin x. I understand I have to use. cos(A +.
Free trigonometric identity calculator - verify trigonometric identities step-by-step
Sin X Pi 2 Identity - Communauté MCMS
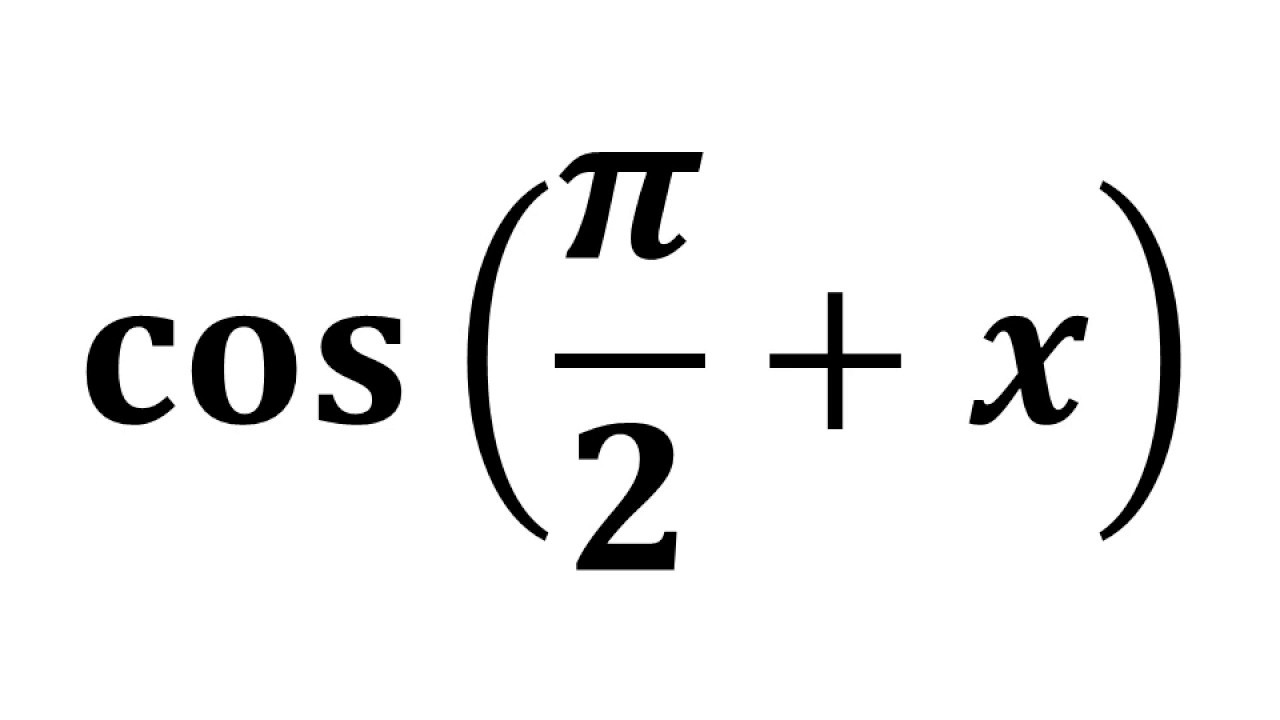

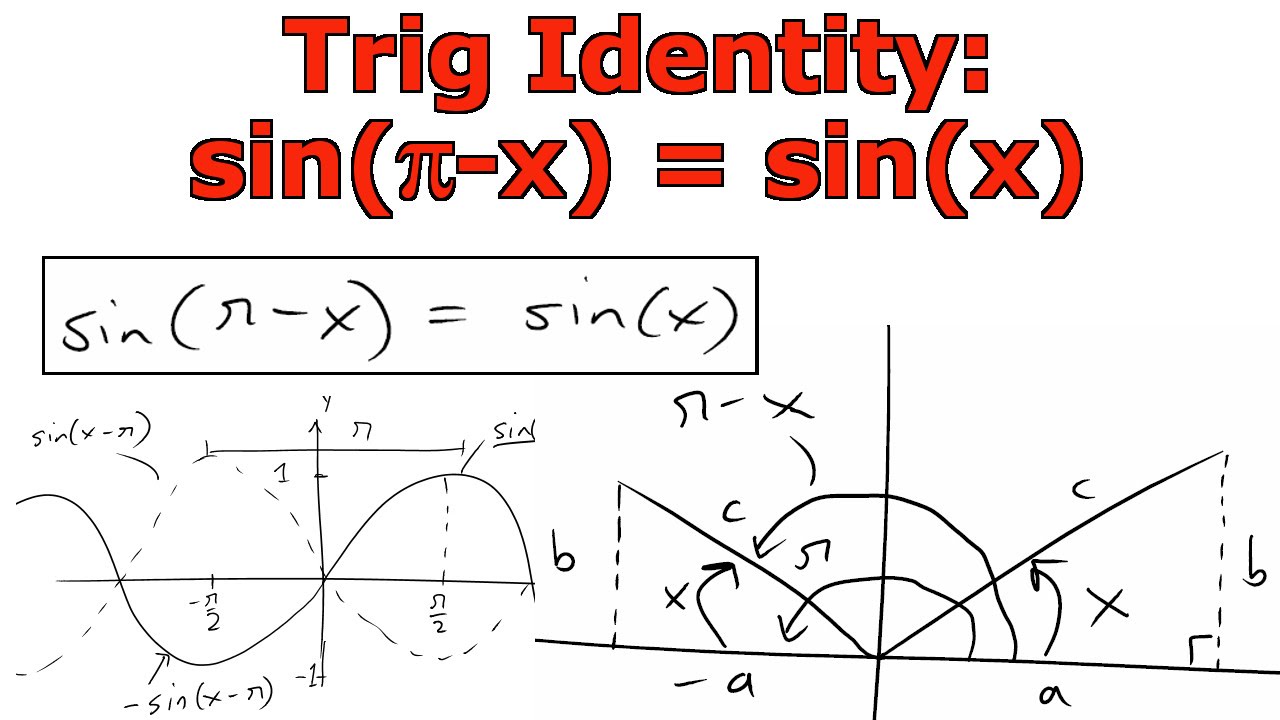




![Sin X Pi 2 Identity [最も共有された! √] π/2 graph 734341](https://useruploads.socratic.org/cmKdoY8sSRu6SEeNLh56_graph30.jpg)
Vous pourriez aussi aimer
- Your Talent Is Mine Chapter 41
- My Short Senpai Is Way Too Cute
- Futsutsuka Mono No Ani Desu Ga
- Parcours De Motricité Maternelle Fiche De Préparation
- Cérémonie D Ouverture Des Jeux Paralympiques : Le Début D une Aventure Extraordinaire
- My Stepmoms Daughter Is My Ex Light Novel
- Gta 6 Date Sortie Casino
- Comment Faire Une Hache Sur Minecraft
- Dessin Page De Garde Cahier Poésie Chant
- Resultats Loto Samedi 29 Avril 2023
- Année De Naissance De Gatien Marcailhou D aymeric
- Page De Garde Pour Le Francais
- When His Eyes Opened Chapter 3068
- Carte Du Monde Avec Pays
- Death Mage Who Doesn t Want A Fourth Time
- Questions Culture Générale Avec Réponses Pdf
- Verbe Rejoindre Au Présent De L indicatif
- Hoeveel Is 1 Newton In Kg
- How To Tame My Beastly Husband Manhwa
- Pages De Garde Evaluations Grand Cahier
